
We all know how to identify at a glance the different parts of most plants, such as the trunk of a tree or the root of any of them. However, do you know well what all the parts of plants are and what functions they perform?
It may seem like basic information, but whether you are starting to study it now or want to refresh your knowledge about plants or expand it, we invite you to join us in this article about the 5 parts of a plant and their functions with diagrams.
In summary, the important parts of plants are these five:
Stem - Roots - Leaves - Flower - Fruit
Next, we will explain each of these parts of plants and their functions.
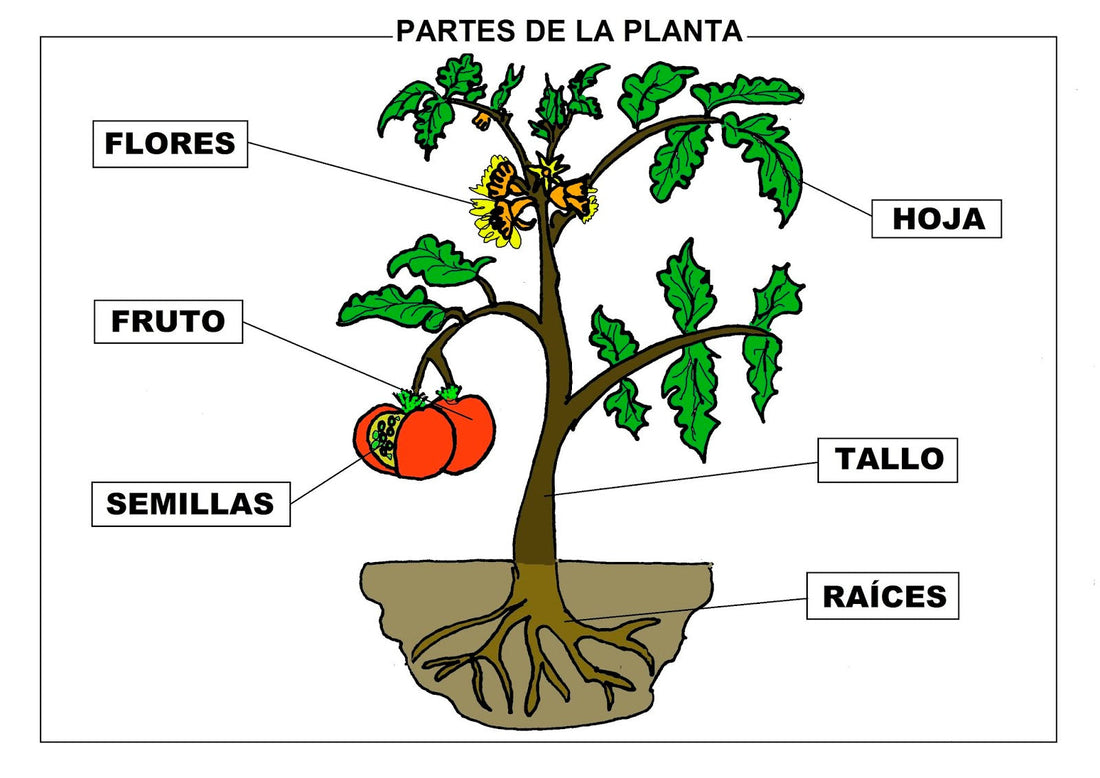
Stem
The stem is the aerial part of the plant that among its functions is to provide support and structure to it, holding its other aerial plant organs, such as leaves and flowers. Another of its main characteristics is that it presents negative geotropism, which means that it grows in the opposite direction to gravity. Although we have mentioned that it is the aerial part of the plant, the truth is that there are several types of stems and their functions:
Types of stems:
Stems can be classified in different ways, but the most common of them is to do so according to the environment in which they are found, which differentiates underground and aerial stems.
The underground stems are further subdivided into:
- tubers
- rhizomes
- bulbs.
Aerial stems can be differentiated into:
- upright
- creeping
- climbers
- fickle
Although there are special stems, such as those with thorns, stolons or tendrils.
Stem functions.
As we have said, one of the two main functions of the stem is to support the entire aerial part of the plant. The other is to transport nutrients and substances throughout the interior of the plant. From the roots, the so-called raw sap rises to the leaves through the ducts of the stem, where it is enriched with carbon dioxide and gives rise to processed sap, the sustenance of the plant.
Root
We can all recognize the roots of most plants: that branched part that is usually found underground and with which it feeds. Let's go a little further:
What are roots and their types Roots are the first organ that plants develop when they germinate, and arguably the most important. There are several types of roots, which can be classified in different ways: Types of roots according to the anchorage they provide to the plant:
- Contractile roots
- Stilts
- Epiphytic roots
Types of roots according to their shape:
- Axonomorphic roots
- fasciculated roots
- Napiform roots
- Branched roots
- tuberous roots
Types of roots depending on the direction of growth:
- Adventitious roots
- aquatic roots
- Sucking roots
- aerial roots
- Storage roots
As we have said, one of the main functions of the roots is to absorb water and nutrients through the small absorbent hairs they have, food that they then transmit to the rest of the plant through the stem. The other function they perform is to anchor the entire structure of the plant to the medium, either with underground roots that grip deeply, or with aerial roots that anchor to other plants or surfaces. Some roots have the ability to photosynthesize, or to attach themselves to other plants to absorb nutrients from them.  Leaves The leaves are one of the most recognizable parts of any plant, and despite their great diversity of shapes, sizes and even colors, they are present in almost all plants and, in addition, the leaves of plants have vital functions, such as photosynthesis, among others.
Leaves The leaves are one of the most recognizable parts of any plant, and despite their great diversity of shapes, sizes and even colors, they are present in almost all plants and, in addition, the leaves of plants have vital functions, such as photosynthesis, among others.
What are leaves and their types:
They are plant organs, usually very thin and green in color, that grow from the branches or stems of plants. They can be classified in many different ways: according to their petiole, their edge, their ribs or even their shape. Its most basic and basic classification, however, is based on whether the plant keeps its leaves all year round, and is perennial, or whether it loses them in the cold months, and is deciduous. Leaf functions
- The leaves mainly fulfill three main functions:
- They carry out photosynthesis, and thus obtain chemical energy from the sun's rays.
- They allow the plant to breathe, exchanging gases at night.
- They can sweat, letting excess water escape through them.
Classification of leaves (according to their shape)  Flower The flower, the most attractive part for people in the case of many plants,is responsible for the reproduction of the plant. That is why, many times, the flowers are of such striking colors: to attract pollinating insects. However, all plants reproduce by flowers. Types of flowers
Flower The flower, the most attractive part for people in the case of many plants,is responsible for the reproduction of the plant. That is why, many times, the flowers are of such striking colors: to attract pollinating insects. However, all plants reproduce by flowers. Types of flowers
There is an immense diversity of types of flowers, of very different sizes, colors, shapes and aromas. Parts of the flower:
The flower has a calyx, corolla, stamens, filament and pistils. In the stamens, the male sexual organ of the plant, pollen is found, which when carried to the pistils, the female sexual organ, gives rise to the process of creating a new plant.

Fruit Not all plants have fruit, but those that reproduce by sexual reproduction by seeds tend to produce it. When the flower has been fertilized, it produces a seed and this forms the fruit around it.



4 comments
excelente cuanto el fruto?
gogoog
gogoog
Excelente tomè de allì algunos puntos para exponer en clase. Gracias, muchas gracias. Dios les bendiga grandemente.